The classification of FRP can be categorized into thermoplastic FRP and thermosetting FRP based on the resin's distinct heat behavior. Furthermore, it can be further classified as quasi-isotropic FRP, bidirectional fiber reinforced FRP, and unidirectional fiber reinforced FRP according to its fundamental type. Additionally, it can also be divided into epoxy FRP, polyester FRP, phenolic FRP, and furan FRP based on its application and characteristics.
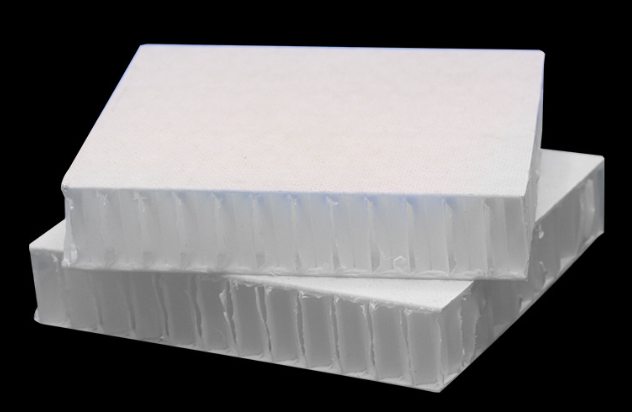

Thermoplastic glass fiber reinforced plastic: This type of glass fiber reinforced plastic possesses a linear or branched chain macromolecular structure. It softens when heated and subsequently melts, allowing it to be shaped as required. After cooling, it hardens and can still soften and melt when reheated at a certain temperature. This plasticizing process can be repeated multiple times.Thermosetting glass fiber reinforced plastic: This kind of glass fiber reinforced plastic transforms into a non-melting solid after heating and curing, rendering it unsuitable for thermoplastic processing.
Basic types:- Quasi-isotropic FRP: Manufactured using chopped fiber felt or molded plastics, this type exhibits similar anisotropic strength characteristics. It is suitable for products with low strength or stiffness requirements or unclear loads.- Bidirectional fiber-reinforced glass-reinforced plastic: Consisting of bidirectional fabric layers, this variant offers higher strength in two orthogonal directions. It is suitable for rectangular flat structures or thin shell structures.- Unidirectional fiber-reinforced FRP: The fibers are arranged in one direction only, making it ideal for applications requiring strict unidirectional forces.Uses and features:- Epoxy FRP: Possesses high mechanical strength and excellent electrical properties.- Polyester fiberglass: Offers cost-effectiveness and good toughness, making it suitable for large components.- Phenolic fiberglass: Exhibits high temperature resistance, making it appropriate for use in high temperature environments.- Furan FRP: Demonstrates good corrosion resistance, thus being well-suited for chemical environments.
These classification methods enable the widespread utilization of FRP across various fields - from construction to industrial equipment; from storage tanks to pipelines - meeting diverse needs with its unique properties.

